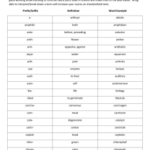
Biology Terms That Start With H
1. Habitat
2. Haemoglobin
3. Halophyte
4. Haploid
5. Heterozygous
6. Homologous
7. Herbivore
8. Homeostasis
9. Hypertonic
10. Hypothesis
11. Hibernation
12. Herbicide
13. Hybridization
14. Heritability
15. Hormones
16. Histology
17. Helicase
18. Hydrophilic
19. Hydrophobic
20. Hemizygous
21. Hemizygote
22. Hydrolysis
23. Hydroponics
24. Homeotic genes
25. Human Genome Project
26. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
27. Horizontal gene transfer
28. Home range
29. Hemoglobinopathy
30. Haplogroup
More About Biology Terms That Start With H
Welcome to the world of biology, where the wonders of life unfold before our very eyes. In this article, we will explore an intriguing collection of biology terms that all have one thing in common – they start with the letter “H”. From the depths of the oceans to the heights of the rainforests, these terms encompass a wide array of fascinating concepts that shed light on the intricate workings of the natural world.
Let us begin our journey with “Habitat”. A habitat refers to the specific place or environment in which an organism lives, providing it with the necessary resources for survival. Each organism is uniquely adapted to its habitat, whether it be a lush forest, a scorching desert, or even the freezing Arctic tundra. The study of habitats allows biologists to better understand the complex relationships between organisms and their surroundings.
Moving on, we come across the term “Heredity”. Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring through genetic information. It is through heredity that offspring inherit characteristics such as eye color, height, or even predisposition to certain diseases. Understanding heredity is essential in comprehending the variation and diversity that exists within populations.
Next, we delve into the realm of “Hormones”. Hormones are chemical substances produced by glands in the body that regulate various physiological and behavioral processes. They act as messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to various target tissues or organs to control functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproductive cycles. Hormones play a critical role in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating the intricate balance of the body.
The term “Hydrolysis” takes us into the fascinating world of chemical reactions. Hydrolysis refers to the process by which a compound is broken down using water molecules. This reaction is essential for many biological processes, such as the digestion of food in our bodies. Enzymes catalyze hydrolysis reactions, ensuring the efficient breakdown of complex molecules into simpler forms that can be readily utilized by living organisms.
As our exploration continues, we encounter “Heterozygous” and “Homozygous” – two terms that are central to the study of genetics. Heterozygous refers to an individual that carries two different alleles for a particular gene, while Homozygous refers to an individual that carries two identical alleles for a specific gene. Understanding the differences between these terms is crucial in comprehending genetic inheritance patterns and the expression of traits.
Now, let us shift our focus to the fascinating world of “Histology”. Histology is the study of the microscopic structure and organization of tissues. By examining tissues under a microscope, histologists can gain insights into the cellular composition, arrangement, and function of different tissues. This field plays a vital role in diagnosing diseases, understanding the development of organs, and unraveling the complexities of the human body.
Lastly, we must touch upon “Homeostasis”. Homeostasis is the ability of an organism or system to maintain a stable internal environment despite external fluctuations. This delicate balance allows living organisms to function optimally by regulating variables such as body temperature, pH levels, and blood sugar. Without homeostasis, biological systems would become unstable, leading to various disorders and ultimately, death.
From habitats to homeostasis, the world of biology teems with captivating terms that open our eyes to the intricacies of life. These terms starting with the letter “H” provide a glimpse into the extraordinary diversity and interconnectedness of the natural world. Whether you are a student, a curious mind, or simply someone seeking to expand their knowledge, exploring these biology terms will undoubtedly deepen your understanding and appreciation of the living world around us. Join us on this exciting journey through biology, where countless wonders await.
Biology Terms That Start With H FAQs:
1. FAQ: What is a habitat?
Answer: A habitat refers to the natural environment or specific area where an organism or a population of species lives and thrives.
2. FAQ: What is a heterotroph?
Answer: A heterotroph is an organism that cannot produce its own food and relies on consuming organic matter from other organisms to obtain energy.
3. FAQ: What is homeostasis?
Answer: Homeostasis is the ability of an organism or a system to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes or fluctuations.
4. FAQ: What is the purpose of a hormone?
Answer: Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by various glands in the body that regulate and coordinate different biological processes and activities.
5. FAQ: What is the role of a herbivore in an ecosystem?
Answer: Herbivores are animals that primarily feed on plants, contributing to the transfer of energy and nutrients from plants to other organisms in the ecosystem.
6. FAQ: What is an allele?
Answer: An allele is a variant form of a gene, usually resulting in different characteristic traits or features in an organism.
7. FAQ: What are the basic components of a DNA molecule?
Answer: A DNA molecule consists of nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine).
8. FAQ: What is the function of the hippocampus in the brain?
Answer: The hippocampus is a region of the brain involved in memory formation, spatial navigation, and learning.
9. FAQ: What is a host in the context of parasites?
Answer: A host is an organism that provides a living environment and sustenance to a parasite, allowing it to live and reproduce.
10. FAQ: What are the implications of habitat loss on biodiversity?
Answer: Habitat loss is a significant threat to biodiversity as it disrupts the natural balance and can lead to the extinction or decline of species that rely on specific habitats for survival.