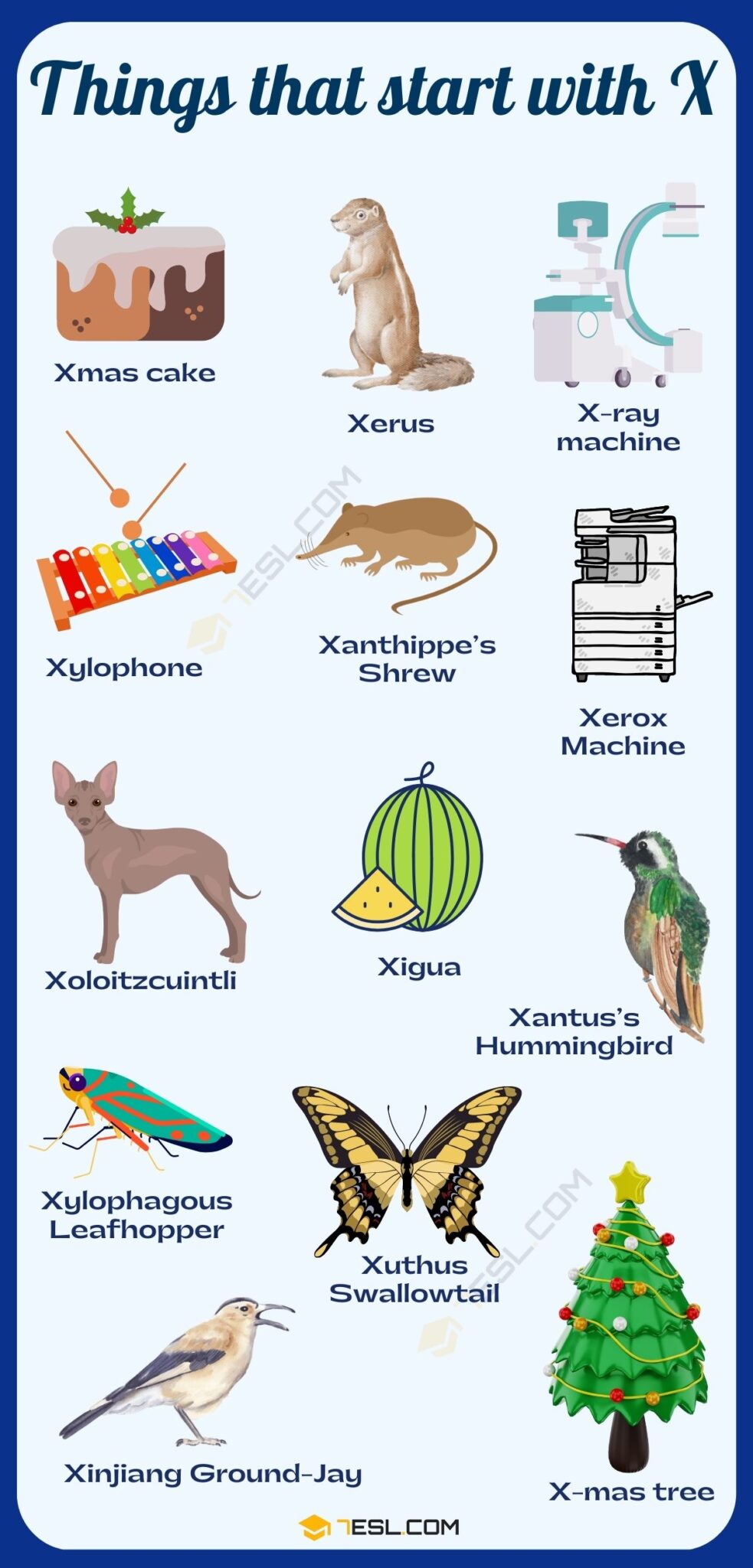
Engineering That Start With X
1. X-ray diffraction analysis
2. Xenon ion propulsion systems
3. X-band radar technology
4. X-ray imaging equipment
5. Xerographic printing machines
6. X-shaped building structures
7. X-ray inspection systems
8. Xenon gas lighting systems
9. Xeriscaping techniques in landscaping
10. X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy
11. Xenolith studies in geotechnical engineering
12. X-Plane flight simulator software
13. X-ray lithography in microfabrication
14. Xenon arc lamps for specialized lighting
15. X-bracing techniques in structural engineering
16. X-band communication systems for satellites
17. X-ray crystallography for material analysis
18. Xenon flash lamps for photography and physics experiments
19. XeroGel thermal insulation materials
20. X-engine aircraft designs with multiple engines
21. X-ray diffraction strain analysis in material testing
22. Xenobots: bioengineered robotic organisms
23. X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanning
24. X-pinch plasma physics experiments
25. Xenon hexafluoroplatinate catalysts in chemical engineering
26. X-pattern seismic surveying techniques
27. X-band microwave components and devices
28. X-ray lithotripsy for kidney stone treatment
29. Xerographic engineering document management systems
30. Xenon ion implantation for semiconductor manufacturing
More About Engineering That Start With X
Welcome, engineering enthusiasts and curious minds, to today’s discussion that begins with the letter X. Engineering, a field that encompasses creativity, innovation, and problem-solving, is a driving force behind the advancements that shape our world. As we delve deeper into the realm of engineering, let us embark on a journey that explores various branches of this vast discipline, shedding light on its significance and how it impacts our daily lives.
X marks the spot where we uncover the extraordinary world of engineering. From the towering structures that grace our skylines to the intricate circuits powering our devices, engineering plays a pivotal role in transforming ideas into reality. It encapsulates the amalgamation of science, mathematics, and technology to engineer solutions that cater to our needs, aspirations, and dreams.
Although some may view engineering as a complex and daunting subject, its essence lies in simplifying complex problems by breaking them down into smaller, manageable components. This systematic approach allows engineers to navigate through challenges and develop innovative solutions that push the boundaries of what is considered possible. By thinking critically and creatively, engineers possess the uncanny ability to turn imagination into tangible creations.
Let us explore a few of the remarkable disciplines that engineering encompasses, as we descend into this captivating world. Starting with the letter X, we encounter fields that might be less known, but undoubtedly fascinating.
Firstly, we venture into the realm of Xenobots, where scientists and engineers merge the boundaries of biology and engineering to create tiny living organisms capable of performing specific tasks. These biobots, constructed from the cells of African clawed frogs, are engineered using sophisticated algorithms that guide their behavior. By harnessing the power of genetics and computational design, these Xenobots have the potential to change the face of medicine, environmental cleanup, and even small-scale manufacturing.
Next, our journey takes us into the realm of X-ray imaging, a groundbreaking technology rooted in engineering principles. X-rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation, allow us to peer through solid objects and capture detailed images of the human body or industrial components. This extraordinary technology, pioneered by engineers, plays a vital role in medical diagnostics, non-destructive testing, and security screening, revolutionizing the way we understand our world.
Finally, we delve into the world of X-band radar, a remarkable application of engineering that finds its place in various domains, including aerospace and meteorology. The X-band represents a specific frequency range of radar signals, which allows for high-resolution images and accurate detection of targets. Engineers leverage this technology to track weather patterns, aid in air traffic control systems, and enhance military operations, pushing the boundaries of observation and situational awareness.
Engineering, an ever-evolving field, continues to shape our world and influence various aspects of our lives. Whether it is the engineering behind cutting-edge technologies, awe-inspiring infrastructure, or groundbreaking scientific discoveries, this discipline plays an inextricable role in our modern society.
So, dear readers, join us in this exploration of engineering, where we shed light on its wonders, unveil its advancements, and inspire the engineer within you. Embrace the spirit of curiosity, as we embark on this journey together, unraveling the magic and innovation that lies within the captivating world of engineering.
Stay tuned for our forthcoming discussions, as we savor the essence of engineering, one letter at a time. Together, let us celebrate the triumphs of human ingenuity, as we continue to build a future shaped by the power of engineering.
Engineering That Start With X FAQs:
1. Q: What is X-ray engineering?
A: X-ray engineering involves the design, development, and application of machinery and systems that use X-rays for various purposes, such as medical imaging, security screening, industrial inspection, and material analysis.
2. Q: How does xenobiology relate to engineering?
A: Xenobiology is a branch of engineering that focuses on the study and manipulation of biological systems that are not found in nature. It combines principles from molecular biology, synthetic biology, and genetic engineering to create novel and useful organisms.
3. Q: What is xerography engineering?
A: Xerography engineering is the field that encompasses the design and development of photocopiers and laser printers, which use the principles of electrostatic charges and toner to produce prints and copies of documents.
4. Q: Can you explain the concept of xylitol engineering?
A: Xylitol engineering involves the production and application of xylitol, a naturally occurring sugar alcohol, through the use of bioprocess engineering techniques. Xylitol has applications in various industries, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and oral care products.
5. Q: What is the role of xenon lighting engineering?
A: Xenon lighting engineering focuses on the design and development of xenon-based lighting systems, which produce intense, high-quality light output. These systems find applications in automotive headlights, cinema projectors, and high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps.
6. Q: What are some key aspects of xerographic printing engineering?
A: Xerographic printing engineering includes the study of key components like photoreceptors, developing units, fusing mechanisms, and image processing algorithms, which together enable the production of high-quality prints through electrostatic-based printing techniques.
7. Q: What is the purpose of X-band engineering in radar systems?
A: X-band engineering focuses on the development of radar systems that operate in the X-band frequency range, typically spanning 8-12 GHz. These radar systems find applications in weather monitoring, air traffic control, and military defense.
8. Q: Can you explain the principles of xenotransplantation engineering?
A: Xenotransplantation engineering involves the study and development of technologies to facilitate the transplantation of organs or tissues from one species to another. This field aims to overcome the shortage of human organs for transplantation.
9. Q: What is the significance of X-ray crystallography engineering?
A: X-ray crystallography engineering plays a crucial role in determining the three-dimensional atomic and molecular structures of various substances. This information aids in understanding the properties and behavior of materials, including proteins, minerals, and chemicals.
10. Q: How does xViewport engineering contribute to virtual reality?
A: xViewport engineering involves the design and implementation of advanced virtual reality (VR) headset systems. These engineering efforts focus on enhancing the resolution, field of view, comfort, and tracking capabilities of VR devices, providing users with more immersive experiences.